37. Mail of the sponsor
You remember the problem “The word of sponsor” from New Year
contest. I remind you briefly that problem: after the event finished, the
sponsor wanted to send out the prizes for winners.
But the postal system is not
perfect and not all the prizes can be delivered to participants. There are n post offices in the
country, numbered from 1 to n. The sponsor sends the prizes from the office
number s. Also, we know the
mail transportation system – the pairs of post offices
between which the mail can be passed.
Before the new competition
the sponsor decided to guarantee the safe delivery of prizes. To do this, the
sponsor is ready to establish new links between some pairs of post offices.
Your task is to find the least amount of new connections, so that prizes can be
delivered after the competition to all participants, regardless of where they
live and which post office use.
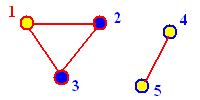
Input. First line contains three
integers – the number of post offices n (1 ≤ n ≤ 105), the number of post
office the sponsor uses s (1 ≤ s ≤ n) and the number of
links between the pairs of offices k (0 ≤ k ≤ 105).
Each of the next k lines
contains 2 numbers: a and b – the numbers of post
offices, between which the mail transportation exists (a and b are
different numbers from interval [1; n]). All the pairs (a, b) are different.
Output. Print one number – the minimum possible
number of new connections to be created, so that the mail can be delivered
from s to any other post office.
|
Sample input |
Sample output |
|
5 1 4 1 2 2 3 1 3 4 5 |
1 |
SOLUTION
disjoint
set
Algorithm analysis
The number of new connections equals to the number
of connected components of the graph minus 1. Since n ≤ 105, to solve the problem we must use a system of disjoint
sets with heuristics.
Algorithm realization
Declare the arrays.
vector<int> parent,
depth;
Function Repr finds a
representative of the set that owns the vertex v.
int Repr(int v)
{
if (v == parent[v]) return v;
return parent[v] = Repr(parent[v]);
}
Function Union unites the sets with
vertices x and y. A set with a lower height joins a set
with a higher height.
void Union(int x, int y)
{
x = Repr(x), y = Repr(y);
if (x == y) return;
if (depth[x] < depth[y]) swap(x, y);
parent[y] = x;
if (depth[x] == depth[y]) depth[x]++;
}
The main part of the program. Read the input data. Initialize
the arrays.
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &s, &k);
parent.resize(n
+ 1);
depth.resize(n +
1);
for (i = 0; i <= n; i++) parent[i] = i;
Read the
edges of the graph. Perform the
Union
operation on a pair of vertices of each edge.
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
scanf("%d
%d", &a,
&b);
Union(a, b);
}
The number of sets equals
to the number of connected components of the graph.
for (c = 0, i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if (parent[i] == i) c++;
Print the
number of new connections that should be built.
printf("%d\n", c - 1);
Algorithm realization – classes
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int i, n, s, k, a, b;
class dsu
{
public:
vector<int> parent,
depth;
dsu(int n)
{
parent.resize(n + 1);
depth.resize(n + 1);
for (int i = 0; i <=
n; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
int Repr(int v)
{
if (v == parent[v]) return v;
return parent[v] = Repr(parent[v]);
}
void Union(int x, int y)
{
x = Repr(x), y = Repr(y);
if (x == y) return;
if (depth[x] < depth[y]) swap(x, y);
parent[y] = x;
if (depth[x] == depth[y]) depth[x]++;
}
int getSets()
{
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <=
n; i++)
if (parent[i] == i) cnt++;
return cnt;
}
};
int main(void)
{
scanf("%d %d %d", &n, &s, &k);
dsu ds(n);
for (i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
scanf("%d %d", &a, &b);
ds.Union(a, b);
}
printf("%d\n", ds.getSets() - 1);
return 0;
}
Java realization
import java.util.*;
public class Main
{
static int parent[], depth[];
static int Repr(int v)
{
if (v == parent[v]) return v;
return parent[v] = Repr(parent[v]);
}
static void Union(int x, int y)
{
x = Repr(x); y = Repr(y);
if (x == y) return;
if (depth[x] < depth[y])
{
int temp = x; x = y; y = temp;
}
parent[y] = x;
if (depth[x] == depth[y]) depth[x]++;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int s = con.nextInt();
int k = con.nextInt();
parent = new int[n+1];
depth = new int[n+1];
for(int i = 0; i <= n; i++) parent[i] = i;
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
Union(a,b);
}
int c = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
if(parent[i] == i) c++;
System.out.println(c - 1);
con.close();
}
}
Java realization – classes
import java.util.*;
class dsu
{
int parent[], depth[];
public dsu(int n)
{
parent = new int[n + 1];
depth = new int[n + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= n; i++)
parent[i] = i;
}
public int Repr(int v)
{
if (v == parent[v]) return v;
return parent[v] = Repr(parent[v]);
}
public void Union(int x, int y)
{
x = Repr(x); y = Repr(y);
if (x == y) return;
if (depth[x] < depth[y])
{
int temp = x; x = y; y = temp;
}
parent[y] = x;
if (depth[x] == depth[y]) depth[x]++;
}
public int getSets()
{
int cnt = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < parent.length; i++)
if (parent[i] == i) cnt++;
return cnt;
}
}
public class Main
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Scanner con = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = con.nextInt();
int s = con.nextInt();
int k = con.nextInt();
dsu ds = new dsu(n);
for(int i = 0; i < k; i++)
{
int a = con.nextInt();
int b = con.nextInt();
ds.Union(a,b);
}
System.out.println(ds.getSets() - 1);
con.close();
}
}